Pressure drop calculation of flowing liquids in pipes
What is fluid pressure drop?
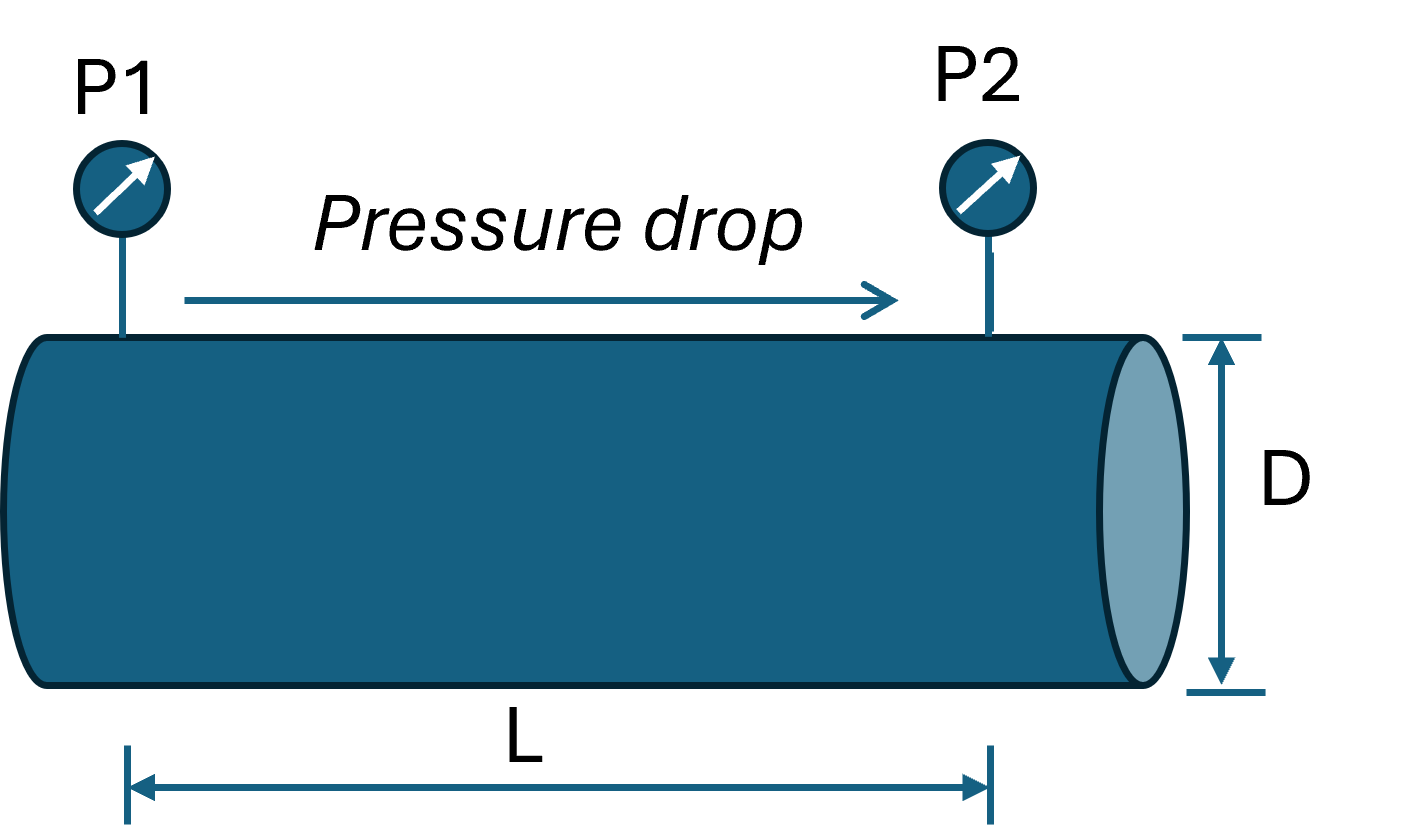
Fluid pressure drop in a pipe is the reduction in pressure as fluid flows from one end of the pipe to the other.
This drop occurs due to friction between the fluid and the inner surface of the pipe, as well as due to any bends, fittings, or changes in pipe diameter that cause resistance to flow.
Mathematically, pressure drop (ΔP) is the difference between the inlet pressure (P1) and the outlet pressure (P2) of the fluid along the pipe length.
Why It’s Important to Calculate Pressure Drop?
System Efficiency: Excessive pressure drop means more energy is required to pump the fluid through the pipe. Calculating and minimizing pressure drop can improve system efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Proper Equipment Sizing: Accurate pressure drop calculations are essential for selecting the right pump size. Underestimating pressure drop could lead to undersized equipment, which may not achieve the desired flow rate, while overestimating can result in unnecessary energy consumption.
Avoiding System Issues: High pressure drops can lead to issues like cavitation, especially in long pipelines, and can affect the performance and longevity of equipment.
Safety: In industrial settings, maintaining appropriate pressure is critical for safe operation, especially in systems that handle high-pressure fluids or hazardous substances.